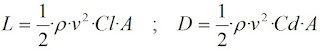Then of MotoGP season 2016 where the all motorbikes y all categories was mount wings.
Today is banned, but I'd like on resume of simple analysis of effects and how it works.
I am sure that in the future the aerodynamics into motorbike have more weight in the design, the aerodynamics is not high relevant value, but in one world, where each tenth could be mark win or lose one race, aerodynamics can provide this tenth.
Aerodynamics basic concepts
Angle of Attack
The main effect is the angle between air and profile depend lifts generate, until one point where profile lost lift and only provide more drag, (stall angle)
 |
| Angle of Attack |
Lift and Drag Equations
For calcule I used information with NACA profiles (this information is public in NASA webs)
Aerodynamic analysis
Wing analysis
 |
| Ducati GP16 courtesy from Ducati |
- Wheelbase 1400mm
- Rear SAG with pilot 30mm
- Fork travel 110mm
- Pitch full brake (fork fully compressed, rear wheel without load, rearshock extended) 5.7º
- Wing area 250mm x 100mm
 |
| Ducati GP13 braking |
In the front part I used a thin profile NACA 65-206. This enter in stall quickly and provide low lift (Cl < 1) (down force) and low drag, this wing was used for Yamaha YZF-M1
- Straight mode with motorbike with full gas we put the Angle of attack (AoA) 6º
- In full brake the motorbike pitch 5.7º, therefore the AoA is 11.7º
 |
| NACA 65-206 charts |
With 11.7º, this profile is in stall, this point is in brake, therefore Drag increase and provide a braking extra. The table provide the several data (10 N ~ 1 kg ~ 2.3 lb)
NACA 65-206
|
6,0º
|
11,7º
| |||||||
100 km/h
|
200 km/h
|
300 km/h
|
350 km/h
|
100 km/h
|
200 km/h
|
300 km/h
|
350 km/h
| ||
L
|
8,14 N
|
32,54 N
|
73,22 N
|
99,66 N
|
2,32 N
|
9,30 N
|
20,92 N
|
28,47 N
| |
D
|
0,46 N
|
1,86 N
|
4,18 N
|
5,69 N
|
1,39 N
|
5,58 N
|
12,55 N
|
17,08 N
| |
In the side part I used a thin profile NACA 6412. This provide high lift (Cl > 1) (down force) and high drag, this wing was used for Ducati GP16
- Straight mode with motorbike with full gas we put the Angle of attack (AoA) 7.5º
- In full brake the motorbike pitch 5.7º, therefore the AoA is 13.2º
 |
| NACA 6412 charts |
With 13.2º, this profile provide more lift, this point is in brake, therefore provide more force to tyres (like a weight) and provide a braking extra. The table provide the several data (10 N ~ 1 kg ~ 2.3 lb)
NACA 6412
|
7,5º
|
13,2º
| |||||||
100 km/h
|
200 km/h
|
300 km/h
|
350 km/h
|
100 km/h
|
200 km/h
|
300 km/h
|
350 km/h
| ||
L
|
17,43 N
|
69,73 N
|
156,89 N
|
213,55 N
|
5,81 N
|
23,24 N
|
52,30 N
|
71,18 N
| |
D
|
0,23 N
|
0,93 N
|
2,09 N
|
2,85 N
|
1,39 N
|
5,58 N
|
12,55 N
|
17,08 N
| |
However, these profiles try to create less drag possible, therefore if you have enough power to waste in drag, you could be increase the Lift forces.
For example we can increase AoA without stall and increse Lift with slots in the profile
In the F1, the top in racing aerodynamics Cl is over 3
 |
| Source Racecar Engineering |
If we calculate with Cl 3
Ranurados
|
Cl 3
| |||
100 km/h
|
200 km/h
|
300 km/h
|
350 km/h
| |
L
|
34,87 N
|
139,46 N
|
313,79 N
|
427,10 N
|
Each wing, generate 43kg with 350km/h, with 4 wings (one front one lateral, in each side) reach 174kg , this is the same weight of one MotoGP without rider
Behavior effects
Another effect is the rider change his position in the bike, this create changes in aerodynamics
 |
| Motorbike Magazine courtesy |
In corner when the rider try to leave the bike vertical and launch his weight to turn side, it create a wall where stop the airstream, and the lateral wing lost efficiency, and the other side create a roll effect like the rider put weight in the opposite side, this effect aid to take the turn.
Other effects in in the brake the pitch increase the Drag and Lift, and this provide more capacity to brake.
The antiwheelie effect, but normally, the speed in the exit is less and this effect is not the more important, beacuse, the wheelie is stronger in short gear, and this translate to low speeds
General drag, the vortex could be create two effects
1º Low the general drag like a golf ball, locate vortex provide less general drag
 |
| Locate vortex decrease the general drag |
 |
| NASA studies |
2º Create a concentre vortex behind the bike, where concentrate turbulence and the motorbike behind shake by this turbulende. The air intake to engine could be affected for this tubulence. In 2016 season riders complained for this effect.
Security
The problem is if wing hit a rider in one accident or overtake. We could see that Force that must withstand so that it does not brake the fairing, therefore it must and hard part and could be injure to riders. Cruchtlow warn this effect, and he has reason.
This is the first reason to ban the wings, other reason is cost increase due to aerodynamics studies.
In the future I will develop other post with how develop aerodynamics forces in the motorbike without wings.